해시 클러스터 테이블
- 클러스터 키 인데스가 해시 함수로 대체.
- 테이블의 데이터가 인덱스 이며, 물리적인 인덱스는 존재하지 않는다.
- 저장형 함수 또는 사용자 제공 함수를 이용하여 로우의 키 값을 해시 처리하여 데이터가 디스크 어디에 존재해야 하는지 계산.
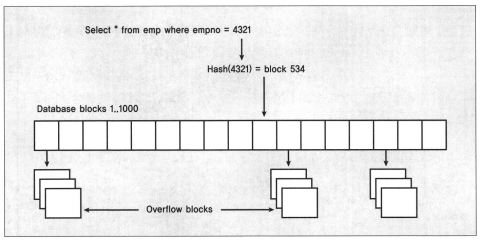
- 범위 스캔을 수행할 수 없다. (=, IN 조건으로만 가능)
- 범위 스캔을 하려면 일반적인 인덱스를 추가해야 한다.
- 해시 테이블의 크기를 기술하기 위해서 hashkeys 옵션을 추가.
- hashkeys값을 이용하여 가장 근접한(크거나 같은) 소수로 생성.
- size와 소수로 수정된 hashkeys 값을 곱한 값으로 클러스터의 전체 공간을 계산하여 할당.
- 데이터의 크기를 포함하는 충분한 공간을 미리 할당(hashkeys/trunc(blocksize/size))
(필요할 때마다 동적으로 필요한 공간을 할당하는 인덱스 클러스터와의 큰 차이.) - 해시 경합이 발생해도 괜찮다.(블록 체이닝 발생 가능성은 증가)
- hashkeys 값은 고정크기. (변경하려면 재생성)
-- 해시 클러스터 생성
create cluster hash_cluster
(hash_key number)
hashkeys 75000
size 150
/
create table t_hashed
cluster hash_cluster(object_id)
as
select * from all_objects
/
alter table t_hashed add constraint
t_hashed_pk primary key(object_id)
/
exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(user, 'T_HASHED');
-- HEAP 테이블 생성
create table t_heap
as
select * from t_hashed
/
alter table t_heap add constraint
t_heap_pk primary key(object_id)
/
exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats(user, 'T_HEAP');
-- 배열을 위한 pkg 생성
create or replace package state_pkg
as
type array is table of t_hashed.object_id%type;
g_data array;
end;
/
-- 배열 채우기
begin
select object_id bulk collect into state_pkg.g_data
from t_hashed
order by dbms_random.random;
end;
/
-- 하드 파싱 수행
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_hashed
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_heap
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
-- runstats 확인
exec runstats_pkg.rs_start();
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_hashed
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
exec runstats_pkg.rs_middle();
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_heap
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
exec runstats_pkg.rs_stop(10000);
Run1 ran in 212 hsecs
Run2 ran in 213 hsecs
run 1 ran in 99.53% of the time
Name Run1 Run2 Diff
STAT...Cached Commit SCN refer 73,844 0 -73,844
LATCH.cache buffers chains 148,032 221,918 73,886
STAT...consistent gets from ca 73,901 11 -73,890
STAT...no work - consistent re 73,893 2 -73,891
STAT...cluster key scan block 73,891 0 -73,891
STAT...cluster key scans 73,891 0 -73,891
STAT...index fetch by key 0 73,891 73,891
STAT...rows fetched via callba 0 73,891 73,891
STAT...table fetch by rowid 2 73,893 73,891
STAT...session logical reads 73,963 221,734 147,771
STAT...buffer is not pinned co 73,895 221,677 147,782
STAT...consistent gets from ca 73,903 221,687 147,784
STAT...consistent gets 73,903 221,687 147,784
STAT...consistent gets - exami 2 221,676 221,674
STAT...logical read bytes from 605,904,896########################
Run1 latches total versus runs -- difference and pct
Run1 Run2 Diff Pct
153,481 231,776 78,295 66.22%
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
--> cpu 시간은 거의 동일
--> 캐시 버퍼 체인 래치 감소에 주목.
-- tkprof
alter session set sql_trace=true;
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_hashed
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
declare
l_rec t_heap%rowtype;
begin
for i in 1 .. state_pkg.g_data.count
loop
select * into l_rec from t_heap
where object_id = state_pkg.g_data(i);
end loop;
end;
/
alter session set sql_trace=false;
********************************************************************************
SQL ID: 6wyqvnr7mkbrv Plan Hash: 1450564094
SELECT *
FROM
T_HASHED WHERE OBJECT_ID = :B1
call count cpu elapsed disk query current rows
------- ------ -------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
Parse 1 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0
Execute 73891 0.65 0.72 0 2 0 0
Fetch 73891 0.57 0.68 0 73891 0 73891
------- ------ -------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
total 147783 1.23 1.40 0 73893 0 73891
Misses in library cache during parse: 1
Optimizer mode: ALL_ROWS
Parsing user id: SYS (recursive depth: 1)
Number of plan statistics captured: 1
Rows (1st) Rows (avg) Rows (max) Row Source Operation
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------------------------------------------------
1 1 1 TABLE ACCESS HASH T_HASHED (cr=1 pr=0 pw=0 time=62 us)
********************************************************************************
********************************************************************************
SQL ID: b6syrq5gcw169 Plan Hash: 2815550882
SELECT *
FROM
T_HEAP WHERE OBJECT_ID = :B1
call count cpu elapsed disk query current rows
------- ------ -------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
Parse 1 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 0
Execute 73891 0.96 0.85 0 0 0 0
Fetch 73891 0.82 0.73 0 221673 0 73891
------- ------ -------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
total 147783 1.79 1.58 0 221673 0 73891
Misses in library cache during parse: 1
Optimizer mode: ALL_ROWS
Parsing user id: SYS (recursive depth: 1)
Number of plan statistics captured: 1
Rows (1st) Rows (avg) Rows (max) Row Source Operation
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------------------------------------------------
1 1 1 TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID T_HEAP (cr=3 pr=0 pw=0 time=28 us cost=2 size=97 card=1)
1 1 1 INDEX UNIQUE SCAN T_HEAP_PK (cr=2 pr=0 pw=0 time=15 us cost=1 size=0 card=1)(object id 79237)
********************************************************************************
--> 해시 클러스터 테이블은 간단히 object_id를 변환하여 데이터 억세스
--> heap 테이블은 인덱스 블럭(cr=2)를 읽고 데이터 블럭을 읽었다. 3배 더 발생.
- 해시 클러스터는 훨씬 적은 I/O를 수행.
- 해시 클러스터 쿼리는 1/3 가량의 버퍼 캐시를 읽더라도 동일한 양의 cpu를 사용. (해시를 수행하는 일은 매우 cpu 집중적인 일)
단일 테이블 해시 클러스터
- 클러스터에는 한 번에 오직 하나의 테이블만이 존재.
- 다른 테이블을 생성하려면 기존에 존재하는 테이블은 drop 해야 한다.
- single table 키워드 추가.
해시 클러스터가 적합한 경우
- 얼마나 많은 데이터가 발생될 것인지 정확하게 알고 있거나, 혹은 구체적인 데이터 발생 최대값을 알고 있는 경우.
- DML, 특히 삽입이 추출에 비해 적은 경우.
- hashkey 조건으로 빈번하게 데이터를 액세스하는 경우.
